TL;DR for busy leaders
Avoid using real production data in tests and never include sensitive data in automated test reports.
ReportPortal addresses confidentiality, integrity, availability, and compliance of reported data.
Security in ReportPortal spans the full lifecycle: secure development, encryption, IAM, retention, auditing, and monitoring.
Test automation reporting tools collect rich contextual artifacts — logs, stack traces, screenshots, and attachments — that may unintentionally include personally identifiable information (PII), secrets, or other sensitive business data. This article outlines potential threat scenarios and describes how ReportPortal helps reduce these risks.
Why Test Reporting Needs Security & Privacy
When you run automated tests, they generate a lot of helpful data for debugging. The problem is some of the data may accidentally reveal information meant to stay private. Sometimes teams slip up and use real information in tests — it happens. That’s why ReportPortal is designed to keep your data safe, even if something sensitive ends up in the reports. And since regulations like GDPR and CCPA plus audits for SOC 2 or ISO 27001 require strict data handling, it’s important to treat test results with the same care as production logs.
Types of sensitive data that commonly sneak into reports:
Logs & stack traces Error messages or SQL queries might expose user IDs, emails, or tokens.
Screenshots A simple UI snapshot could show personal details, payment info, or internal URLs.
Environment variables Automated tests often rely on environment variables for configuration, such as API keys, database URLs, or feature flags. If these variables are logged, captured in reports, or included in attachments, they can expose sensitive information unintentionally.
Secrets in test code Hard-coded credentials or temporary keys left behind for convenience.
Typical risk scenarios:
Screenshot leak A test screenshot catches a customer email or card number and then gets stored in a shared project.
Long-lived artifacts Some logs or attachments stick around forever, carrying sensitive details.
Excessive permissions Someone gets assigned the wrong role — for example, a Project Manager instead of a Member — and can accidentally modify important settings.
Security isn’t something you enable once — it’s a continuous process that runs through every layer of the product and every phase of its lifecycle. From how features are developed to how data is stored, accessed, and monitored, ReportPortal applies security best practices end to end.
Secure Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
Even when sensitive data is reported, ReportPortal ensures data safety and security. This is achieved through a process that covers every stage — from design and coding to testing, deployment, and operations:
Secure architecture Threat modeling, security risk assessments and security impact analyses are conducted to identify where sensitive data flows and what controls are needed. Detailed architecture documents and diagrams can be shared with customers under NDA.
Secure development Developers receive training on secure coding, PII/GDPR awareness and how to avoid anti-patterns that leak secrets. The codebase is scanned regularly with static analysis tools to catch common issues (unsafe deserialization, hard-coded secrets, insecure logging).
Secure testing Application security is tested continuously: static analysis + dynamic scans, and bi-annual penetration tests to validate controls against current threats.
Secure deployment Encryption in transit and at rest is enforced. Deployments follow recommended best practices from cloud providers and include infrastructure hardening — such as secure network segmentation, strict access policies, regular patching, and vulnerability management. Encryption of data in transit is done via TLS for UI/API.
Secure operations Segregation of duties and least-privilege access are enforced operationally. Infrastructure monitoring and alerting (SIEM, metrics dashboards such as Grafana) surface anomalous behavior. Data retention and lifecycle policies limit exposure from stale artifacts.
Annual security audit Once a year, ReportPortal undergoes a comprehensive audit covering secure development practices, testing procedures, and deployment processes. This review ensures that security controls remain effective, up to date with evolving threats, and aligned with compliance requirements.
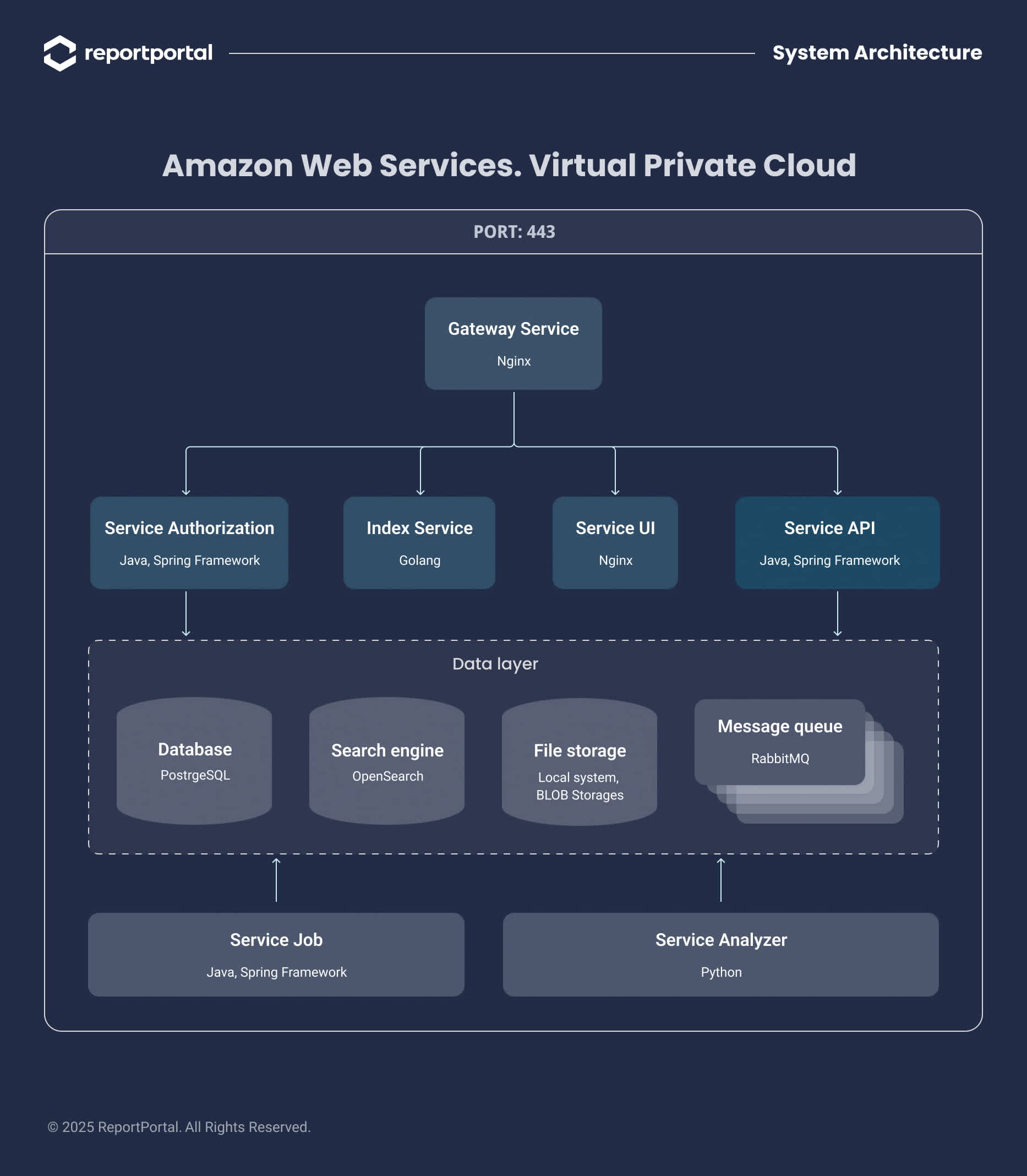
Identity & Access Management (IAM)
Proper identity and access controls are the first line of defense.
Authentication ReportPortal supports enterprise SSO integrations (SAML, LDAP, Active Directory).
Authorization Data is organized by projects. Role-based access control lets you assign roles such as Project Manager, Operator, Customer, Member — each role has scoped permissions (view, edit). Apply least privilege: give users the minimum role needed. ReportPortal also offers SCIM Server feature, which automates user provisioning and project assignments. This reduces manual work and minimizes the risk of errors during account setup and role management.
API access Users create personal access tokens for automation and CI. Tokens are revocable and you should enforce token rotation policies.
Session management Instance-level timeouts are configurable, so inactive sessions automatically expire. When combined with SSO and conditional access policies, session controls reduce the risk from stolen or unattended sessions.
Retention & Deletion
Controlling how long artifacts live is essential to limiting risk.
Configurable retention Launches, logs, screenshots and attachments have configurable retention period.
Automated cleanup Scheduled cleanup jobs remove artifacts past their retention window. This prevents accumulation of long-lived secrets.
Inactive user cleanup & right to be forgotten Automated policies can remove inactive users after a configurable period. ReportPortal supports “right to be forgotten” flows: an instance variable can enable account deletion, and deleting a user removes personal data associated with that account. Additionally, SCIM integration enables automatic deprovisioning of accounts, ensuring that user access is revoked immediately — without waiting for the retention period to expire.
Auditability & Monitoring
You cannot protect what you cannot see. Robust auditing and monitoring are built in.
Event monitoring Project-level and instance-level event streams record membership changes, role updates, token creation/revocation, and administrative operations.
Audit logs Audit logs capture who changed, exported, or deleted data. These trails are essential for forensic investigations and for proving compliance during audits.
Governance & Compliance
ReportPortal is open-source solution, giving you full flexibility without vendor lock-in. Our test automation results dashboard supports different operational models so customers can align governance with their security and compliance requirements.
Self-hosted Gives full control over the stack, network boundaries, and data residency. Customers have security controls and are responsible for patching and configuration. If you’re considering this option, check out our article for insights on what self-hosting really involves.
Managed (dedicated/shared) hosting ReportPortal handles infrastructure and operations. Managed offerings can include hardened defaults and optional compliance artifacts.
Common Pitfalls (and Fixes)
Even with robust security controls in place, teams can still encounter common challenges in test reporting. The following examples highlight frequent issues and practical ways to address them:
Secrets in stack traces Add test-runner filters and regex scrubbing to redact credentials before report submission. Implement pre-publish hooks that scan artifacts for secrets. Check out the guide for practical steps on excluding sensitive information from logs in ReportPortal.
Overshared projects Apply least-privilege roles within the project and regularly review permissions.
Never-expiring artifacts Enforce retention and lifecycle policies. Avoid marking many launches as “important” unless necessary.
“God-mode” API tokens Issue scoped tokens (CI tokens limited to a single project and specific actions) and set rotation schedule.
Real production data in tests Substitute synthetic data or use anonymization/obfuscation tools such as TDSpora.
How to Configure ReportPortal Securely
To ensure that your ReportPortal instance is secure and compliant, follow these essential configuration steps:
Network/TLS setup Configure your network properly, including reverse proxies if needed, and provision certificates to enforce TLS for UI and API traffic.
At-rest encryption Enable encryption for all stored data, including logs and attachments, and implement key rotation policies to maintain security over time.
Identity management Integrate SSO using SAML, LDAP or Active Directory. Local accounts should be used only as a break-glass accounts.
Roles and permissions Define roles per project and create least-privilege templates to ensure users have only the access necessary for their tasks.
Retention policies Set configurable retention rules for launches, logs, and attachments to limit exposure of sensitive data.
Audit logging and alerting Use audit log dashboards and configure alerts to monitor critical actions, such as role changes, or unusual activity.
Test reporting is a critical part of the software development process, but it comes with unique security and privacy challenges. ReportPortal provides a comprehensive set of controls — from development practices and encryption to identity management, retention policies, and auditing — to help teams protect sensitive data throughout its lifecycle. By following best practices, configuring your instance carefully, and regularly reviewing access and retention policies, you can minimize risks, maintain compliance, and ensure that test artifacts remain both useful and protected.